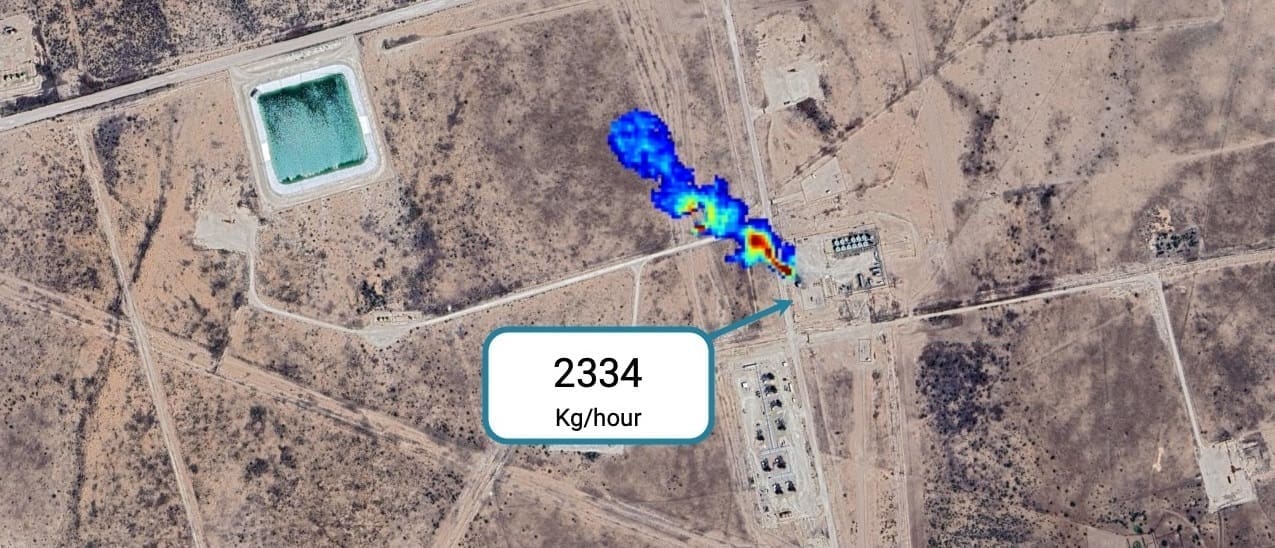
Methane might seem like an easy target for emission control. However, detecting methane leaks is challenging due to several factors:
- Invisible and Odorless: Methane is both colorless and odorless, unlike CO2, which has a distinctive odor. This makes methane leaks hard to identify without specialized equipment.
- Widespread Emissions: Methane leaks can occur throughout the oil and gas value chain, from extraction to storage. The numerous potential leak points complicate detection efforts.
- Remote Locations: Many oil and gas infrastructures are in remote areas, making leaks less visible and harder to monitor regularly.
- Detection Difficulties: Methane molecules are tiny, easily dispersing and mixing with air, complicating detection in low concentrations or windy conditions.
- Technological Limitations: Existing detection technologies have limitations. For instance, infrared cameras require sunlight to function, limiting their use at night or on cloudy days. Other technologies provide only a snapshot, making it hard to quantify total methane emissions over time.
In addition, methane might be considered “lower on the detection chain” urgency as it doesn’t directly harm human health. However, its significant impact on climate change makes its detection crucial. Methane is over 25 times more effective than carbon dioxide at trapping heat over a 100-year period, substantially contributing to global warming.
Improved regulations and investments in detection technologies are essential to address this invisible threat. Despite the above challenges, advancements are being made. Satellite monitoring shows promise for wider and more accurate methane leak detection.
Methane’s Significant Impact
Methane is the second-largest contributor to climate change. Currently, 60% of methane emissions are due to human activities, with the energy sector being the second-largest source. In 2022, the global energy industry released 135 million tonnes of methane.
One staggering example is the recently detected methane super-emitters in Turkmenistan. Methane leaks alone from Turkmenistan’s two main fossil fuel fields were estimated to have caused more global warming in 2022 than the entire carbon emissions of the UK. Countless others across the globe are going undetected at this very moment.
Climate Impact of Methane
Methane’s structure makes it 80 times more harmful than CO2 for two decades after its release, though it remains in the atmosphere for about 12 years compared to CO2’s thousands of years. A 45% reduction over the next decade would help keep global warming under the 1.5-degree threshold set by the Paris Agreement.
Economic Impact of Methane Emissions
Wasted methane from leaks costs the global gas industry about $60 billion in lost revenue annually.
For example, a 2018 study found that the methane leaking rate from oil and gas operations is 2.3%. If that methane could be captured and sold to chemical makers and manufacturers, natural gas producers would increase their revenues by an estimated $188 million yearly.
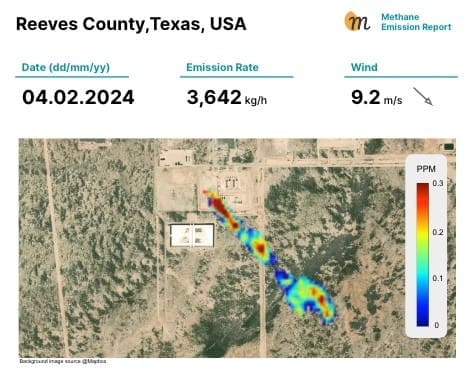 Addressing the Methane Data Blind Spot
Addressing the Methane Data Blind Spot
Accurate data on methane emissions is crucial for effective reduction strategies. Industries often lack information on when and where emissions occur. Estimates suggest that the actual amount of methane emissions is much higher than reported, indicating a significant data blind spot.
Global Efforts to Reduce Methane Emissions
In the US, the Biden Administration has allocated $20 Billion for methane emissions reduction. The plan, unveiled at last year’s COP27 climate conference, includes 50 specific regulatory measures backed by more than $20 billion in new investments to tackle methane emissions.
Funding for the plan will be derived from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act, which includes a first-ever national methane emissions fee of $900 per metric ton of methane for some oil and gas facilities that will go into effect in 2024 and increase to $1,500 per metric ton of methane in 2026.
The Way Forward
To make regulation and compliance possible and to drastically reduce global methane emissions, precise detecting and monitoring technologies are essential. Startup companies are at the forefront of this fight, offering technology that empowers stakeholders to address methane emissions effectively with evidence-based and data-driven decision-making and policy.
Precision in methane monitoring enables decision-makers to take fast action to handle methane emissions. Early detection of methane leaks in oil and gas operations allows for rapid repairs and mitigation efforts, preventing further releases into the atmosphere and potential environmental disasters like super emitters. Near-real-time monitoring capabilities also empower companies to make informed decisions in their emission reduction strategies, measure and verify their performance, and contribute more effectively to the global fight against climate change.
Daniel Kashmir is the CEO and Co-Founder ofMomentick, an emissions intelligence company helping companies detect their emissions using space imagery on a global scale. Prior to establishing Momentick, he spearheaded three tech ventures as founder and CEO, leading one of them to acquisition.
With over ten years of experience in the tech sector, Daniel is a passionate and visionary leader who strives to create innovative and impactful solutions for global challenges, driven by the vision of making a net-zero future a reality.