Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies like machine learning and natural language processing are gaining inroads in the commodity trading arena to analyze data faster and spur more informed decision-making
Artificial intelligence (AI) is all around us and you may not even notice. As stated by Bernard Marr in Forbes, “Artificial intelligence is the broader concept of machines being able to carry out tasks in a way that we would consider ‘smart’.” These machines gather and analyze large amounts of data and then act intelligently based on the conclusions made.
In recent years, AI has been adapted to the commodity trading world. Gone are the days of scratch pad notes and hours of gathering and correlating market data. Commodity trading is inherently a fast-paced environment and always has been. Utilizing technologies such as Intercontinental Exchange’s ICE Chat, which was one of the first electronic market platforms in the early 2000s, has been crucial to gain efficiency. Keeping up with the latest trends, companies are now exploring different areas of AI and incorporating them into their everyday business activities.
Currently, there are two AI technologies trending in the commodity trading arena:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
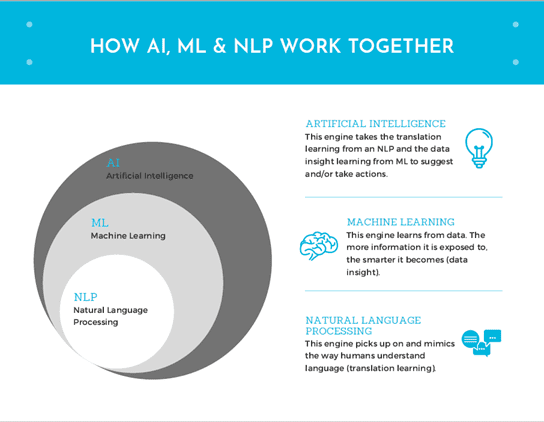
NLP is a technology that picks up on and mimics the way humans understand language. NLP technology can sift through thousands of documents, emails, messaging platforms and phone conversations in seconds. Essentially every type of communication a trader uses to execute throughout the day is harnessed and translated based on a trader’s lingo. Because of its ability to sift through structured and unstructured data (i.e. structured data such as market prices and unstructured such as emails, communications, etc.), it can cut through all the noise and point out trends and key information for the user to take into consideration. Some NLPs can create summaries based on the data evaluated in a user-friendly format that’s easy to understand.
Benefits of NLP technologies include cutting down on manual processes for the users. It captures the data a user typically must enter in a deal capture system, thus also minimizing the risk of human error. This technology also reduces operational risk by collecting the contractual obligations a user makes throughout the day and noting it as a source of evidence for compliance purposes. According to a 2019 Statista report, revenues from the worldwide NLP market will reach over $43 billion in 2025. NLPs are more widely being accepted because they improve productivity and aid in analyzing and finding relationships between data quickly and effectively.
- Machine Learning (ML)
Another popular technology under the AI umbrella is ML. ML is exactly what it sounds like; it’s a machine that learns from data and the more information it’s exposed to, the smarter it becomes. As time goes on and the more data that’s collected, the better these machines become at forecasting and predicting outcomes. When applied to commodity trading, it creates the opportunity for quicker and more educated decisions in a short period of time.
Like NLPs these machines can gather data from thousands of venues, including external and internal sources, market data and even big data (i.e. a massive set of unstructured and structured data). It gives the users suggestions based on historical trends and knowledge of what types of deals a trader typically executes. Over time, AI becomes more valuable due to its wider range of historical knowledge of the operational and market data collected. With its predictive analytical capabilities, it can solve issues quickly, which increases productivity for its users. The tool allows traders to spend less time gathering and analyzing data and more time taking advantage of opportunities a human alone may not always see. Lastly, because of ML’s learning capabilities, trading organizations don’t have to spend time, effort and capital reprograming the system every time data changes.
 Leveraging Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing To Enable Better Commodity Trading
Leveraging Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing To Enable Better Commodity Trading
When leveraging AI technology in the commodity trading space you may find that most systems include both NLP and ML technologies. When paired together, they create a unified “smart” system that can not only pick up on specific words and phrases traders use, but it can also learn from all of the data traders deal with on a daily basis.
Because of the fast nature of trading, most traders don’t have time to enter in a deal right after a deal is agreed upon. This can present a challenge because they may not recall all the specifics and, therefore, may make mistakes when entering details into the deal capture system. AI technology gives the user the ability to reduce these potential pitfalls by streamlining the deal capture process so that trades can be entered while it’s still fresh on their mind, in turn saving them time and generating more accurate data. The solution helps avoid the significant impacts these inconsistencies may have on downstream functions such as schedulers, risk and accounting—each of which may be impacted by deal entry errors that are often key inputs to their daily processes.
There are software offerings in the market that specifically tailor to more efficient and streamlined commodity trading. As one example, Venus Technology Ventures Mistro is an NLP and ML technology that was created by former traders. It’s configured to understand commonly used trading language. Due to its ML capabilities, it learns very quickly what types of deals a trader would typically perform. Admins and/or users can also add specific language used on their trade floor into its dictionary. Once configured, the internal dictionary picks up on keywords and phrases and translates them into something that can be leveraged for other processes and applications.
For example, Mistro could then process that information and populate the fields within a deal capture system accordingly. The system will then make educated guesses on other fields based on a trader’s historical behavior. After all fields have been filled in the user interface screen, the user can then verify the details and finalize it into the deal capture system. The more a user enters in similar types of deals, the more the ML technology knows what types of deal details to enter. This allows it to capture each deal more accurately and completely.
Incorporating AI solutions within commodity trading increases productivity and saves time through automation. Every day a trader uses multiple forms of communication—sometimes simultaneously—to execute deals. Whether it’s through messaging platforms, emails or phone calls, it’s difficult for a trader to remember all the details of a specific deal. AI, and NLP and ML specifically, can help facilitate the process of gathering information from these disparate sources and then take appropriate actions based on this information.
Commodity trading and the downstream energy sector are just now warming up to the idea of implementing AI into their everyday activities. Although there will be cost and time associated with implementing any new technology, there are clear benefits to be gained from effort reduction, costly rework and analytical insights that can provide a return on investment.
The commodity trading world looks dramatically different than it did even 10 years ago. AI will undoubtably play a pivotal role in the evolution of commodity trading over the next 10 years and beyond.
Macey Noon is a Consultant in Opportune LLP’s Process & Technology practice. She has worked with an emphasis in the hydrocarbon commodity industry with a focus on business analytics, trading and risk management process and system selection/implementation. Macey graduated from Texas A&M University with a BBA in Finance and a certificate in Commercial Banking in May 2018. She’s also a certified Salesforce Administrator and a certified Salesforce Platform App Builder Consultant.






