Automated pipe welding has been little more than a pipe dream for decades. But advances in several critical technologies, including sensors, AI (Artificial Intelligence), and collaborative robotics, have converged to create a perfect storm of opportunity—and it’s happening just in time.
The shortage of pipe welders in the U.S. has become a chokepoint for the oil and gas industry. Aging generations of experienced welders are retiring twice as fast as companies can find replacements, younger welders aren’t entering the field, and a steady cadence of layoffs has driven many experienced workers to leave the industry for more dependable career paths. The impact extends beyond the oilfields, however, with the shortage of trained welders also impacting the cost and availability of new equipment. The shortage of pipe welders leads to higher salaries and overtime, and suppliers are struggling to meet demand without enough skilled workers. Oil and gas companies have few options: buying equipment from overseas vendors adds costs and lead time that urgent projects can’t absorb.
In the U.S., the situation is being addressed by moving fabrication to specialized pipe shops to increase efficiency and output over sending workers into the field, and taking advantage of robotic automation for processes that are difficult to fill with human workers. But pipe welding is one of the last tasks to be automated. The dimensional variation of standard V butt weld joints requiring full penetration, single-sided welding necessitates intelligent sensing and adaptive control to ensure the long-term strength and viability of welds in the field, refineries, or factories. Until now, the technologies to accomplish that weren’t viable.
Sensors, Artificial Intelligence, and Collaborative Robots Converge
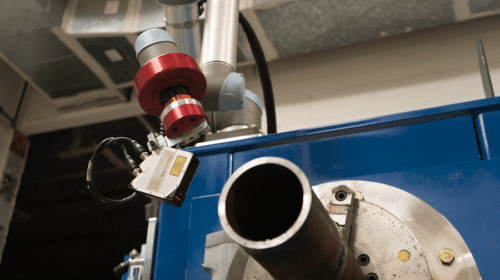
The convergence of several critical technologies has changed that. Today’s laser sensors are small, portable, precise, and affordable enough to be used for challenging tasks such as scanning a pipe’s root opening for a weld. Powerful artificial intelligence software is now accessible to quickly process the sensor data and generate an automated welding program. The final piece of the puzzle is a small, flexible, and safe collaborative robot (“cobot”) that can work alongside a human worker and perform consistent, high-quality welds.
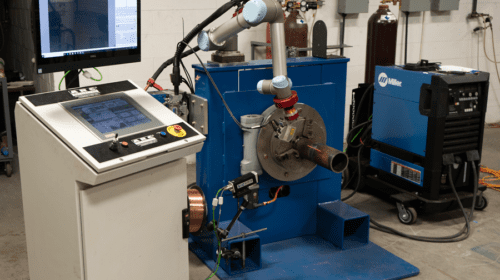
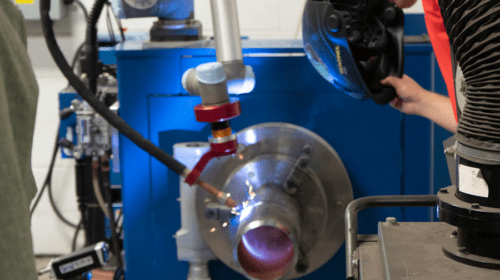
ARC Specialties, a Houston-based developer of welding solutions, debuted the first Artificial Intelligence Pipe Welding (AIPW) system at the Offshore Technology Conference in May 2019. The AIPW pre-scans the root opening using a Micro-Epsilon 2D laser, then the software uses the data to generate the robot path and welding parameters. The system automatically compensates for gap variations the same way a human welder would, by making changes in oscillation, torch position, travel speed, and welding conditions. A Universal Robots 6-axis UR5 robot positions the torch over a tack weld to start the arc to ensure 100 percent root weld acceptance. Fill and cap pass programs are optimized to fill the groove using user-selectable weave or stringer-bead welding techniques. The UR5 is small enough to be portable yet still allows full freedom of motion for both the laser scanner and welding torch. The AIPW uses the Miller Auto Continuum welding power supply to weld the root with regulated metal deposition (RMD), then switches to pulsed spray for the fill and cap passes. This combination of gas metal arc welding techniques maximizes welding productivity while producing X-ray quality, full-penetration pipe welds.
Historically, ARC Specialties declined these tough jobs because joint fit-up was never repeatable. President Dan Allford remarks that in the past, “Only human welders with a ‘golden arm’ able to compensate for variation in root openings, weld center lines, and groove volumes could handle this challenge.” But with new technologies available and no labor-shortage solution in sight, ARC Specialties developed an intelligent machine that incorporates the extensive pipe-welding knowledge of the company’s team of certified welders, along with full robotic motion and welding control. The collaborative aspect of the industrial cobot allows a human with varying levels of experience to work alongside the welding system, establishing the initial weld position and assuring quality throughout the process.
Welding in the shop allows the pipe to be rotated for easier and more consistent access to the weld, and the robot can work continuously, producing much higher duty cycles than human workers, as well as greater repeatability and precision. Moving pipe welding out of the field and automating the process in a shop environment allows manufacturers to optimize both the robot and employees: The AIPW system becomes a force multiplier of the skill and production capability of the welder. Experienced welders can apply their knowledge by overseeing automated welding processes without the physical demands of manual welding. And new welders can be trained on the system as well, with the opportunity to observe the robot’s consistent, perfect technique to learn the process. This is a key advantage of collaborative robots: multiplying the productivity of employees by moving them to higher-value tasks while the robot improves output, quality, and consistency on processes that are difficult to fill with human workers.
The portability and safety of the cobot means the AIPW can easily be skid-mounted and moved as needed, providing valuable flexibility. When the robot is freed from the constraints of one location in the shop and can work in any booth beside a welder, it becomes a tool rather than a fixed system. The tool is not the axis around which production orbits, which is the case in traditional automation.
The Rise of Cobots In Welding Applications
The AIPW is the latest in ARC Specialties’ collaborative welding systems, following the success of its SnapWeld collaborative MIG welding system that takes full advantage of cobot features.
Collaborative welding solutions remove typical automation barriers to entry, such as cost, complexity, and space. In exchange for lower payload capacities compared to traditional robots, cobots offer several benefits that support their increasing use in welding applications. Cobots, which make up the fastest-growing segment of robotics today, are much smaller, lighter, and less expensive than traditional robots, and have built-in safety mechanisms that allow them to be used alongside human workers without safety fencing (after a risk assessment). Lightweight cobot welders can be mounted on tabletops, carts, or skids, can be hung from ceilings, or installed into existing manual welding booths, eliminating the need for costly new robotic cells. This offers far greater flexibility than manual welders or traditional fixed robots. Many designs can be deployed 50 percent faster than traditional robots and often cost less than an annual employee wage.
Unlike traditional robots that require engineer-level programming, cobots are designed for simple programming with a touchscreen-based interface. Welding tasks can be programmed in as little as half an hour by workers who have no previous experience, and programs can be saved and reused, eliminating the expense of ongoing integration support. In many cases, a worker can reprogram a cobot simply by moving the robot arm through the desired motions; the cobot remembers the instruction and repeats it independently, without the need for new code. That allows manufacturers to easily and inexpensively adapt to temporary jobs or burst production during busy seasons. The flexibility and ease-of-programming of cobot-based welding systems make them especially well-suited for low-volume/high-mix environments, as well as custom or small-template welding processes. While collaborative robots are designed for easy programming, they also have full capabilities for sophisticated integrations, and with high accuracy and repeatability, these systems can also handle long runs with consistent quality.
While traditional robot work cells often require considerable customization, the flexibility of a cobot translates to significantly faster return on investment that is often measured in weeks or months. This fast ROI is a function of the technology’s lower capital and minimal disruption to a factory layout, and by multiplying the value of human assets, freeing workers to tackle higher-productivity processes and acquire new skills.
The Time for Automated Pipe Welding Has Come
Automated welding solutions result in higher duty cycles and much more consistent repeatability than manual welding. This increases output and quality and can significantly decrease post-weld clean-up, as well as control the usage and costs of welding consumables. While pipe welding has been elusive until now, the convergence of key technologies means the industry finally has a viable, safe, and cost-effective approach to addressing the welding labor shortage, both in the field and in the shop.
Mitch Dupon is an application development engineer at Universal Robots, with a degree in graduated welding engineering from Conestoga College in Canada. His automation experience spans roles at Panasonic Factory Automation, KUKA Robotics, and Universal Robots. During that time, he has traveled the world installing and implementing welding automation.