Deal activity in 2019 has largely revolved around the need to improve company finances and reduce debt. It drove multinational oil and gas companies, such as ExxonMobil, ConocoPhillips, and Chevron, to review their global operations and begin divesting non-profitable ventures, according to GlobalData, a leading data and analytics company.
The company’s latest report, ‘M&A in Oil and Gas – 2020’, evaluates how oil and gas companies are utilizing mergers and acquisitions (M&A) to realign their businesses with respect to changing market scenarios.
Ravindra Puranik, Oil & Gas Analyst at GlobalData, comments: “During the oil price downturn of 2014–2017, many exploration and production (E&P) companies were able to receive refinancing from investors for about six to seven years amid hopes of price recovery. However, oil prices have not risen sufficiently enough while the debt raised by operators is nearing its repayment period in the next two years. This is raising alarms across the global oil and gas industry, and influencing deal activity. Many companies are starting to show capital prudence, and are resisting from making rash acquisitions. A classic example of this change of approach was Chevron, which stayed away from starting a bidding war with Occidental Petroleum over Anadarko Petroleum.”
Divestment appeared as prominent global trend among several oil and gas companies worldwide during 2019. Throughout the year, companies focused on selling assets to exit from non-profitable ventures or from weak competitive positions in the market. This is likely to enable companies to focus on core businesses and reduce debt levels.
Puranik adds: “Recently, oil and gas companies have focused on prioritizing their areas of operations more on markets closer to their traditional bases. Hence, we are likely to see the UK or European operators acquiring assets in the North Sea, or the US-based companies and oil majors targeting independent shale drillers.”
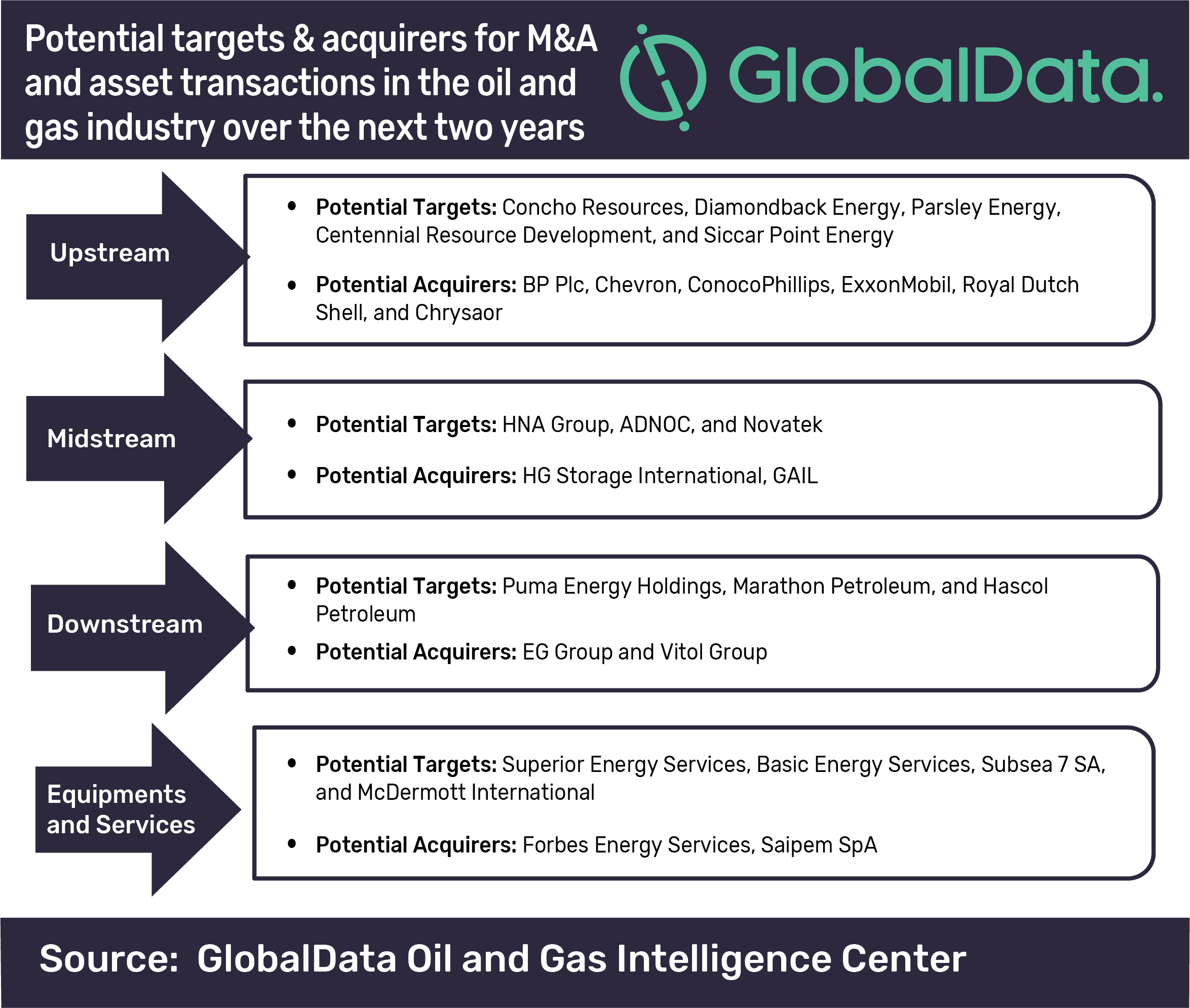
GlobalData’s thematic research identifies such companies within the oil and gas industry that are likely to offer either a part or the entire company for sale in the coming two years across the value-chain. It includes independent shale drillers, such as Concho Resources, Diamondback Energy and Parsley Energy; and midstream and downstream operators, such as HNA Group, Novatek Puma Energy, and Hascol Petroleum which may divest a partial stake in the near future.
Environmental concerns and stricter norms imposed by authorities are further restricting the carbon-intensive industry from operating in specific geographic areas. As a result, in 2019, companies also announced their exits from projects that generate high carbon emissions or are located in ecologically sensitive areas.
Puranik concludes: “Oil and gas giant BP announced to sell its entire business in Alaska to Hilcorp Energy for a total consideration of US$5.6bn. The deal included sale of BP’s upstream portfolio of Prudhoe Bay oil fields in the Alaska North Slope and associated midstream assets in the region. This divestment is likely to help BP in reducing its net methane emissions from global operations.”
About GlobalData
4,000 of the world’s largest companies, including over 70% of FTSE 100 and 60% of Fortune 100 companies, make more timely and better business decisions thanks to GlobalData’s unique data, expert analysis and innovative solutions, all in one platform. GlobalData’s mission is to help our clients decode the future to be more successful and innovative across a range of industries, including the healthcare, consumer, retail, technology, energy, financial and professional services sectors






