Mexico’s high production can be had due, in part, to its high amount of reserves and prospective resources. As of September 2017, the country is sitting on 69.2 billion barrels of crude oil of which 37.3 billion barrels are conventional and 31.9 billion barrels are unconventional. Additionally, the country holds 217.9 trillion cubic feet of natural gas of which 76.4 trillion cubic feet are conventional and 141.5 trillion cubic feet are unconventional. In addition, Mexico also has vast reserves of oil equivalent, which approximate 112.8 billion barrels of equivalent
Top 3 crude oil plays
The highest concentration of crude oil reserves are held in the resource play Tampico-Misantla, with 31.1 billion barrels. Golfo Profundo contains 19.1 billion barrels, and Cuencas del Sureste has the third highest level of reserves with 13.1 billion barrels. The latter two plays are conventional and the former, Tampico-Misantla is unconventional.
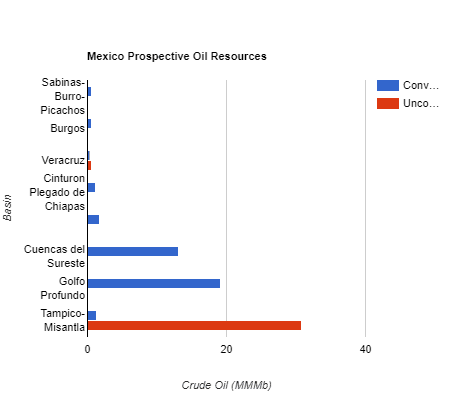 Source: National Hydrocarbons Commission – Mexico
Source: National Hydrocarbons Commission – Mexico
Top 3 natural gas plays
Sabinas-Burro-Picachos (SBP) is the largest natural gas play in Mexico with 68.9 trillion cubic feet of gas reserves, followed closely by Burgos with 67.0 trillion cubic feet of gas and Golfo Profundo with 44.4 trillion cubic feet of natural gas. SPB and Burgos are predominantly unconventional reserves, whereas Golfo Profundo is 100% conventional.
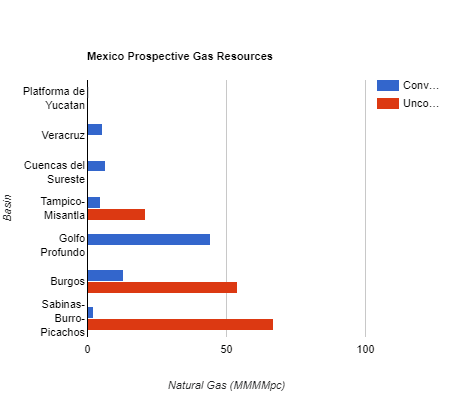 Source: National Hydrocarbons Commission – Mexico
Source: National Hydrocarbons Commission – Mexico
Reserves by region and field
The associated graph, dated January 1, 2017, displays the five regions of Mexico’s oil and gas reserves and further breaks them down into the 14 major fields that comprise Mexico’s oil and gas industry. The data indicate that the northern terrestrial region and northern offshore regions are Mexico’s largest fields by reserves. The following numbers are the original 3P volumes.
The two most famous offshore fields are Cantrell and Ku-Maloob-Zaap with 38.29 billion and 40.59 billion barrels of oil, respectively. The northern offshore fields collectively equal to 78.88 billion barrels of oil and comprise 28.17 trillion cubic feet of gas.
The northern region is composed of four major fields, the two largest are Aceite Terciaio del Golfo with 58.16 billion barrels of oil and Poza Rica-Altamira with 33.57 billion barrels of oil. The entire northern region holds as much as 93.31 billion barrels of oil and 118.48 trillion cubic feet of natural gas.
When assessing a country’s oil and gas reserves the engineering terms P1, P2, and P3 are used. These terms can be defined as follows:
- P1 is proven reserves (proved developed reserves and proved undeveloped reserves.
- P2 contains P1 and adds probable reserves. This is proven and probable reserves.
- P3 is the sum of P2 (proven and probable) plus possible reserves.
Reserves can grow as geology is better understood, more fields are discovered or there is a change in technology which allows for more hydrocarbon extraction from the basin.
Eissler, former editor-in- chief of Oil & Gas Engineering magazine, previously worked as an editor for Dubai-based The Oil & Gas Year Magazine.










