In 2018, trust across institutions—business, government, NGOs and the media—among members of the U.S. general population declined by nine points—the steepest drop ever measured in the United States by the Edelman Trust Barometer. But the drop was even more dramatic for the American natural gas industry—a 13-point decline in trust among the general population and a 25-point drop among the informed public. That stunning drop cannot be ignored—especially as the global industry convenes in Washington this week for the 27th World Gas Conference.
With global energy markets, domestic grid resilience, state and federal policies, activism and politics shaping the natural gas landscape, Edelman conducted further research into the perceptions of natural gas and the natural gas industry within the United States. The findings of this deep-dive were discussed at a recent Natural Gas Perspectives event hosted by Edelman and featuring input from the U.S. Department of Energy, Axios and sector leaders from throughout the natural gas value chain.
Explaining the drop in public trust is complicated and, on the surface, rife with contradiction:
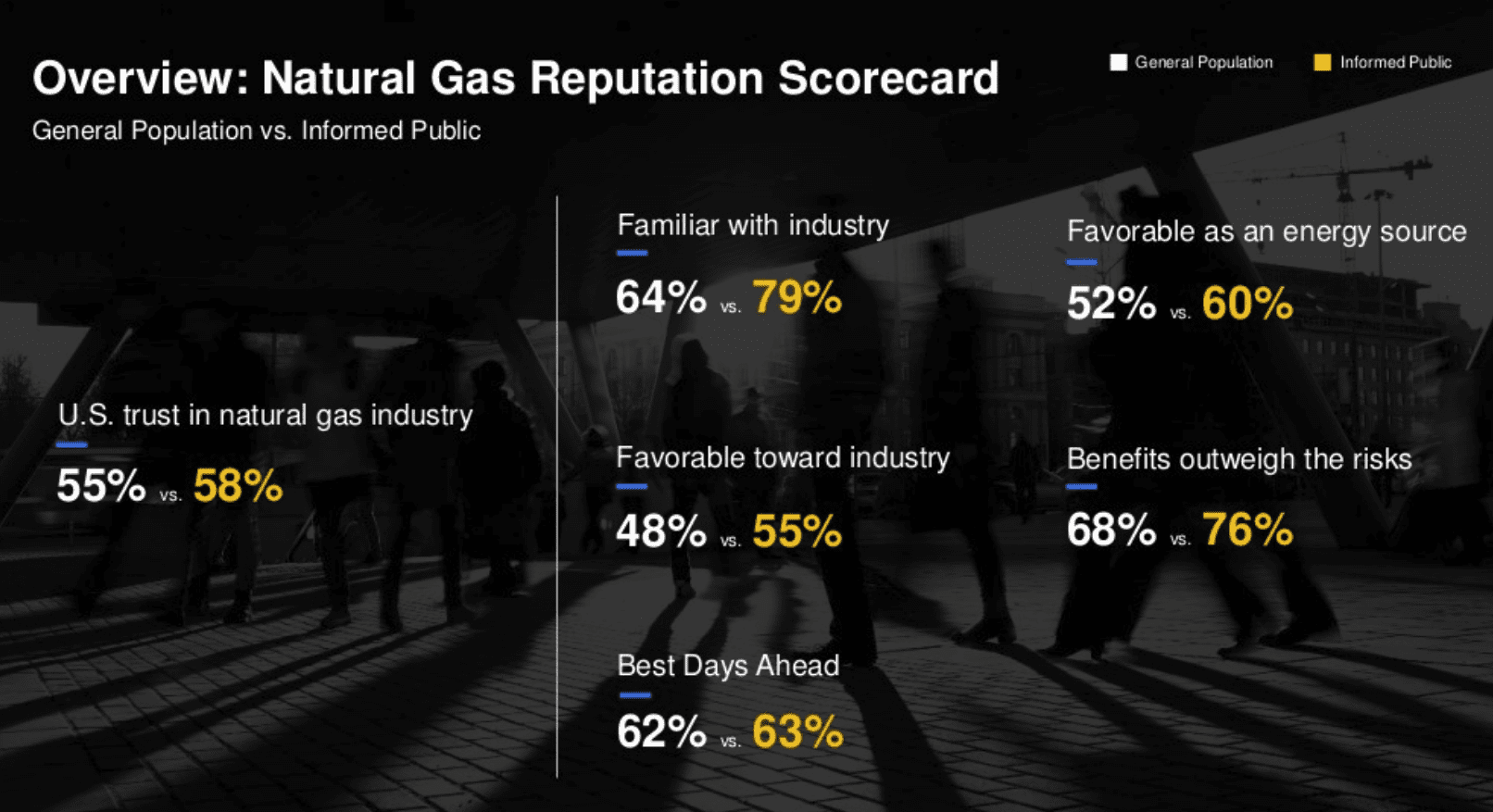
- Less than half of the general population—and only 55 percent of the informed public (a neutral position)—are favorable toward the natural gas industry; but more than 60 percent of both audiences believe the industry’s best days are ahead.
- While only 52 percent of the general population and 60 percent of the informed public are favorable toward natural gas as an energy source (below 60 percent registers as neutral), significantly more believe the benefits of natural gas outweigh the risks (68 percent for the general population and 76 percent for the informed public).
- Contributions toward better air quality are considered among the top benefits of natural gas by both audiences; conversely, emissions released during the natural gas production process—in addition to concerns about extraction technologies—are ranked among its top drawbacks.
- Both audiences overwhelmingly support modernizing the electric grid, and both favor natural gas production and its greater use in electricity, but neither audience supports the actual policies that would make this happen—a classic American dilemma.
[slideshare id=102725952&doc=u-180620164130]
How can people who enjoy the benefits of natural gas—its affordability, abundance and lower emissions—and possess optimism about its future still have such reservations about the broader industry and the continued production of and reliance on natural gas?
Consider how much has changed over the last decade. Ten years ago, the shale revolution was in its infancy. Today, we’ve undergone a complete transformation of America’s energy reality—from scarcity to abundance, from import-dependence to becoming the world’s number one producer of natural gas and an exporter to 30 countries. For those who remember energy rationing and gas lines, the 180-degree role reversal cannot be overstated. The future beyond what U.S. Energy Secretary Rick Perry terms our “astonishing energy miracle” looks very different too—with global demand for liquefied natural gas expected to increase and even exceed supply. Education has not kept pace with this paradigm shift or the innovations that enabled it. Perceptions of natural gas are a reflection of education and often misinformation, and perceptions play a pivotal role in determining policies that will optimize and fortify America’s energy future and impact our geopolitical standing.
Education is the industry’s opportunity to shift perception, and it requires substance, smarts and agility. And further, since the very notion of “facts” is vulnerable to interpretation, and concern over fake news abounds (more than seven in 10 Americans worry about false information being used as a weapon), education and communication from credible industry representatives is imperative. Today, more than ever before, trust is currency.
To paraphrase one of the attendees at our recent Natural Gas Perspectives event, for there to be trust in industry, there has to be confidence in the rules that govern industry. There also has to be a regular, and localized articulation of the industry’s benefits and what it’s going to take to maximize and preserve them. Here is where industry and stakeholders can start:
Amplify positive news
Both Edelman’s research and the conversation at the Natural Gas Perspectives discussion show that benefits of natural gas—on the environmental front in particular—haven’t penetrated the public consciousness, or at least have not done so in ways that overwhelm perceived drawbacks or upend misperceptions.
Even while people’s exposure to natural gas news trends positive, the intensity of any support is very soft—and the window is closing. Industry must get these stories—stories of declines in greenhouse gas emissions, of carbon capture and sequestration innovation, of local economic recovery—in front of key audiences by meeting them where they get their news.
Highlight natural gas as the foundation for a clean energy future
Natural gas has been seen by some as a “bridge” or temporary fuel, though others question the need for a bridge in the first place. In reality, natural gas can be seen as a mutually beneficial foundation upon which renewables have been integrated into the grid. Emphasizing the renewable/natural gas relationship is an asset for industry and will tap into overwhelming favorability rates for the renewable electric industry (in the U.S., 71 percent favorability among the general population and 83 percent among the informed public).
Localize the benefits of natural gas and prepare local cases for infrastructure needs
The very technologies that enabled the shale revolution are drivers of industry mistrust. Mistrust at the macro level leads to specific projects being challenged and stalled at the local level. Similarly, the very infrastructure needed to shore-up, expand and export the benefits of the shale revolution are lighting rods for activism and NIMBY-ism (“not in my backyard” local concerns).
In addition to emphasizing the better-known benefits of natural gas—its affordability, abundance and air quality improvements—locally, it matters to share how U.S. manufacturing has undergone a competitive rebirth because of natural gas. Local jobs—outside of the energy industry—depend on access to natural gas.
While many recognize that infrastructure deficiencies and bottlenecks pose a huge challenge for the future of natural gas in America and while both surveyed audiences support modernizing America’s electric grid to accommodate even more natural gas, only 53 percent of the informed public and just 46 percent of the general population support permitting for new natural gas pipelines. Awareness of the regional and consumer benefits of infrastructure expansion is a necessary precursor to infrastructure policy change and specific project approvals.
Natural gas has rewritten America’s energy story, and rapidly at that. In order to advance public policy that complements innovation and fully capitalizes on the potential of natural gas, industry must work to address and restore declines in public trust. The natural gas story is powerful, and the benefits are there. Americans need to see and believe them. The World Gas Conference is shining a light on some of these stories and broader industry progress, but the task of communicating with and educating the American people is a much longer and higher stakes proposition. Industry should embrace the challenge of helping the country and the world better understand its work and role in the global energy renaissance.
To request a presentation of Edelman’s Natural Gas perspectives data or to speak with us about the findings, please contact: Amy Hemingway, Executive Vice President – Energy, at amy.hemingway@edelman.com or +1 (202) 350-6661.
Oil and gas operations are commonly found in remote locations far from company headquarters. Now, it's possible to monitor pump operations, collate and analyze seismic data, and track employees around the world from almost anywhere. Whether employees are in the office or in the field, the internet and related applications enable a greater multidirectional flow of information – and control – than ever before.


![Why Enhanced Geothermal Energy Could Be Your Next Smart Investment [2025 Guide]](https://b1006343.smushcdn.com/1006343/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Why-Enhanced-Geothermal-Energy-Could-Be-Your-Next-Smart-Investment-2025-Guide-500x280.jpg?lossy=2&strip=1&webp=1)





